Thread Standards Explained: Key Differences and Application Guide for NPT and ISO 7-1 Threads
2025-08-19 15:49:11
In the field of industrial piping connections and mechanical manufacturing, the precise selection of thread standards directly impacts sealing performance and operational safety. This article focuses on two internationally common tapered sealing threads—NPT and ISO 7-1—and explores their standard characteristics, application areas, and selection points to help engineers quickly identify differences and avoid misuse.
I.
Standard Systems and Core Characteristics
1.
NPT Threads: Representative of the American Standard System
Background: Originating from the National Pipe Thread (NPT) standard in the United States, it is the mainstream standard for industrial connections in North America.
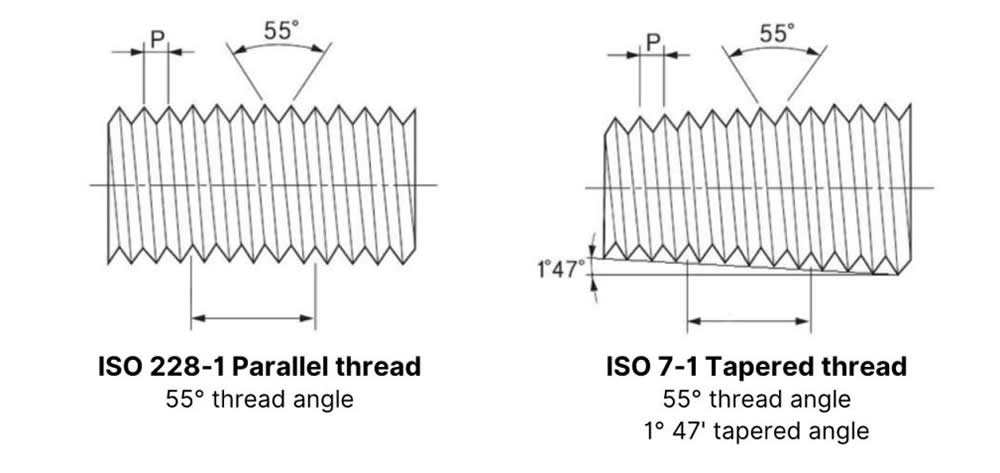
Thread Form: Both internal and external threads have a 1/16 taper (taper angle approx. 1°47′), achieving sealing through tight taper-to-taper contact without the need for additional sealing elements.
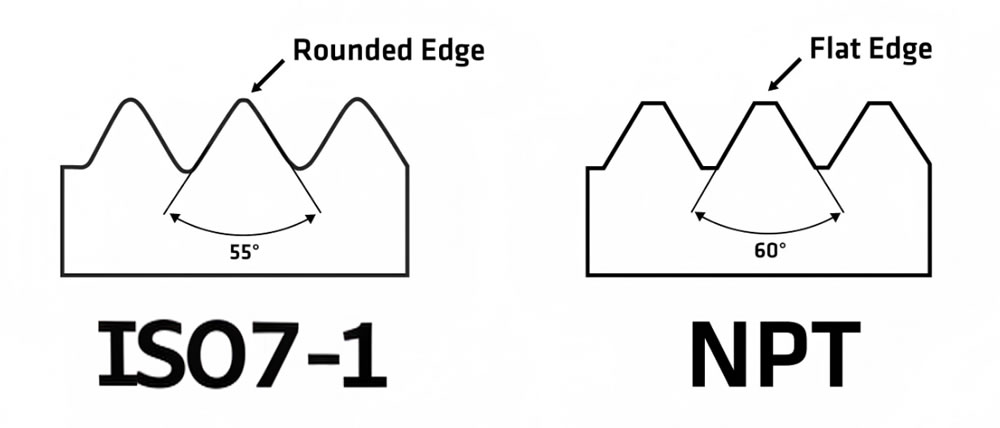
Thread Design: Thread angle is 60°, with a “flat crest and flat root” profile; pitch is measured in threads per inch (TPI), fully compatible with the imperial size system.
System Characteristics: Independent of other international standards, forming a self-contained system.
2.
ISO 7-1 Threads: International Standard for British Tapered Threads
Background: ISO’s standardized definition of the British Standard Pipe Taper (BSPT) thread, widely used in countries and regions adopting the imperial system.
Thread Form: Also 1/16 taper, relying on taper contact for sealing.
Thread Design: Thread angle is 55°, with a “rounded crest and rounded root” typical of imperial threads; pitch is also measured in TPI.
Paired Usage: Often used together with ISO 228-1 BSPP parallel internal threads to form an “external taper + internal parallel” connection for improved stability.
II.
Application Areas
Typical NPT Applications (primarily in the American Standard system):
l
Energy and Chemical: Oil, natural gas, and chemical pipelines; suitable for high-pressure media.
l
Hydraulic and Pneumatic: Engineering machinery and pneumatic equipment; strong cross-device compatibility.
l
Heavy Machinery: Oil and water connections in mining and metallurgical equipment; resistant to vibration and pressure fluctuations.
Typical ISO 7-1 Applications (primarily in the international imperial system):
l
General Machinery Manufacturing: Machine tools, compressor piping; used together with BSPP threads.
l
Water Treatment and Municipal Engineering: Corrosion-resistant, compatible with 316 stainless steel investment castings.
l
Automation and Precision Equipment: Pneumatic control systems and medical devices; meets international interoperability requirements.
·
III.
Selection Points: Differences Mean They Cannot Be Intermixed
Different Thread Angles: NPT 60° vs ISO 7-1 55°—mixing them can result in excessive thread engagement clearance, leading to seal failure.
Different System Compatibility: NPT is for the American Standard system only, while ISO 7-1 requires pairing with BSPP internal threads.
Recommendation: Choose based on project regional standards, media pressure, and equipment compatibility. When in doubt, refer to standard documentation or seek technical support.
Precision in industrial connections starts with understanding standards. We will continue sharing practical knowledge on thread technology to help companies improve engineering quality and efficiency. For more details on the application of thread standards, please contact our technical team for customized solutions.
previous_pagefirst page
next_pageWhat is the main function of the valve?
<
ALL>